DemoBot: Efficient Learning of Bimanual Manipulation with Dexterous Hands From Third-Person Human Videos
arXivAbstract
This work presents DemoBot, a learning framework that enables a dual-arm, multi-finger robotic system to acquire complex manipulation skills from a single unannotated RGB-D video demonstration. The method extracts structured motion trajectories of both hands and objects from raw video data. These trajectories serve as motion priors for a novel reinforcement learning (RL) pipeline that learns to refine them through contact-rich interactions, thereby eliminating the need to learn from scratch. To address the challenge of learning long-horizon manipulation skills, we introduce: (1) Temporal-segment based RL to enforce temporal alignment of the current state with demonstrations; (2) Success-Gated Reset strategy to balance the refinement of readily acquired skills and the exploration of subsequent task stages; and (3) Event-Driven Reward curriculum with adaptive thresholding to guide the RL learning of high-precision manipulation. The novel video processing and RL framework successfully achieved long-horizon synchronous and asynchronous bimanual assembly tasks, offering a scalable approach for direct skill acquisition from human videos.
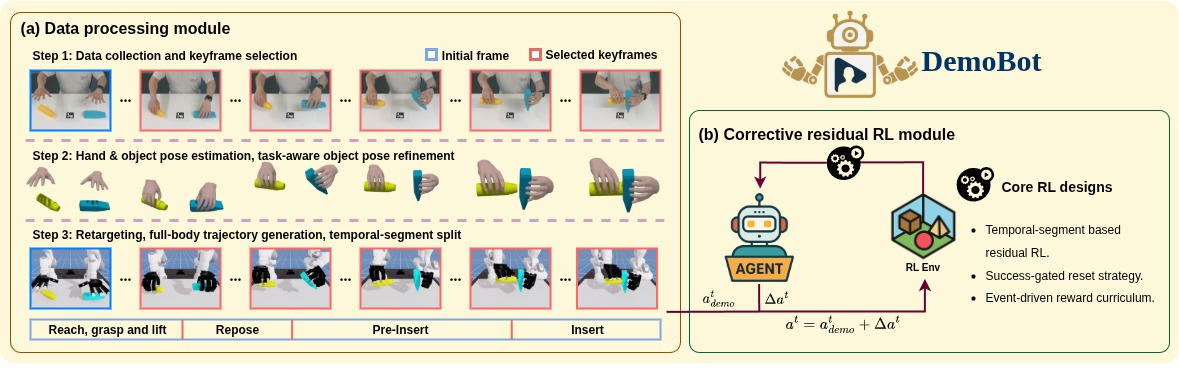
Data processing module
This video demonstrates the workflow of the data processing module of DemoBot, which is designed to extract and refine hand-object motion priors from the visual demonstration. This module leverages hand pose estimator and object pose estimator individually and later align the estimations into the same coordinate system. Additionally, a task specific object pose refinement module is designed to improve the accuracy of object pose for tasks that require high-precision, e.g. insertion task.
Residual corrective RL results -- Simulation
These videos show the results of the policy learned with our residual corrective RL module in IsaacLab simulator. As it can be clearly seen from these videos, the extracted hand-object motion priors are sub-optimal, which is inevitable, as the critical physical contact information between hands and objects can not be recorded by the visual demos. Thus, we designed this residual corrective RL module to learn and compensate this crucial missing part by interacting with physical simulation. The core idea behind this module is straightforward: The robot has to learn how to grasp and manipulate the objects correctly so that it can reproduce the object motions as human did in the demonstration.
Residual corrective RL results -- Real-world setup
These videos show the results of the policy learned with our residual corrective RL module on real-world setup. Limited by the hardware, we can only demonstrate the sim-to-real transferrability of the learning policy with a single-arm robot. In these experiments, the policy is trained in simulation but with several domain randomization tricks applied, including the one to simulate the non-ideal behavior of real-world actuators.
Conclusion
In summary, this study serves as a pioneer for developing an effective framework for learning bimanual dexterous manipulation skills from arbitrary internet video, which is validated through extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world setup. Such a framework demonstrates its effectiveness at a system-level of engineering and integration, using techniques ranging from visual-based hand reconstruction, object pose estimation, to a novel demo-augmented residual reinforcement learning.
Moreover, this work presents a significant step toward scalable robot learning. By extracting motion priors from a single, imperfect human video, DemoBot bypasses the data bottleneck of teleoperation. Our results demonstrate that combining suboptimal motion priors with residual RL enables robots to master contact-rich, long-horizon tasks—problems that are intractable for RL from scratch due to exploration complexity, yet too costly for imitation learning due to data requirements. This paradigm opens the door to leveraging internet-scale video data, moving us closer to general-purpose robots capable of acquiring new dexterous skills by simply `watching' humans.
Video Presentation
BibTeX
@misc{xu2026demobot,
title={DemoBot: Efficient Learning of Bimanual Manipulation with Dexterous Hands From Third-Person Human Videos},
author={Yucheng Xu and Xiaofeng Mao and Elle Miller and Xinyu Yi and Yang Li and Zhibin Li and Robert B. Fisher},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.01651},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.01651},
}